The Glenohumeral Joint Capsular Pattern: Understanding Its Importance in Health and Rehabilitation
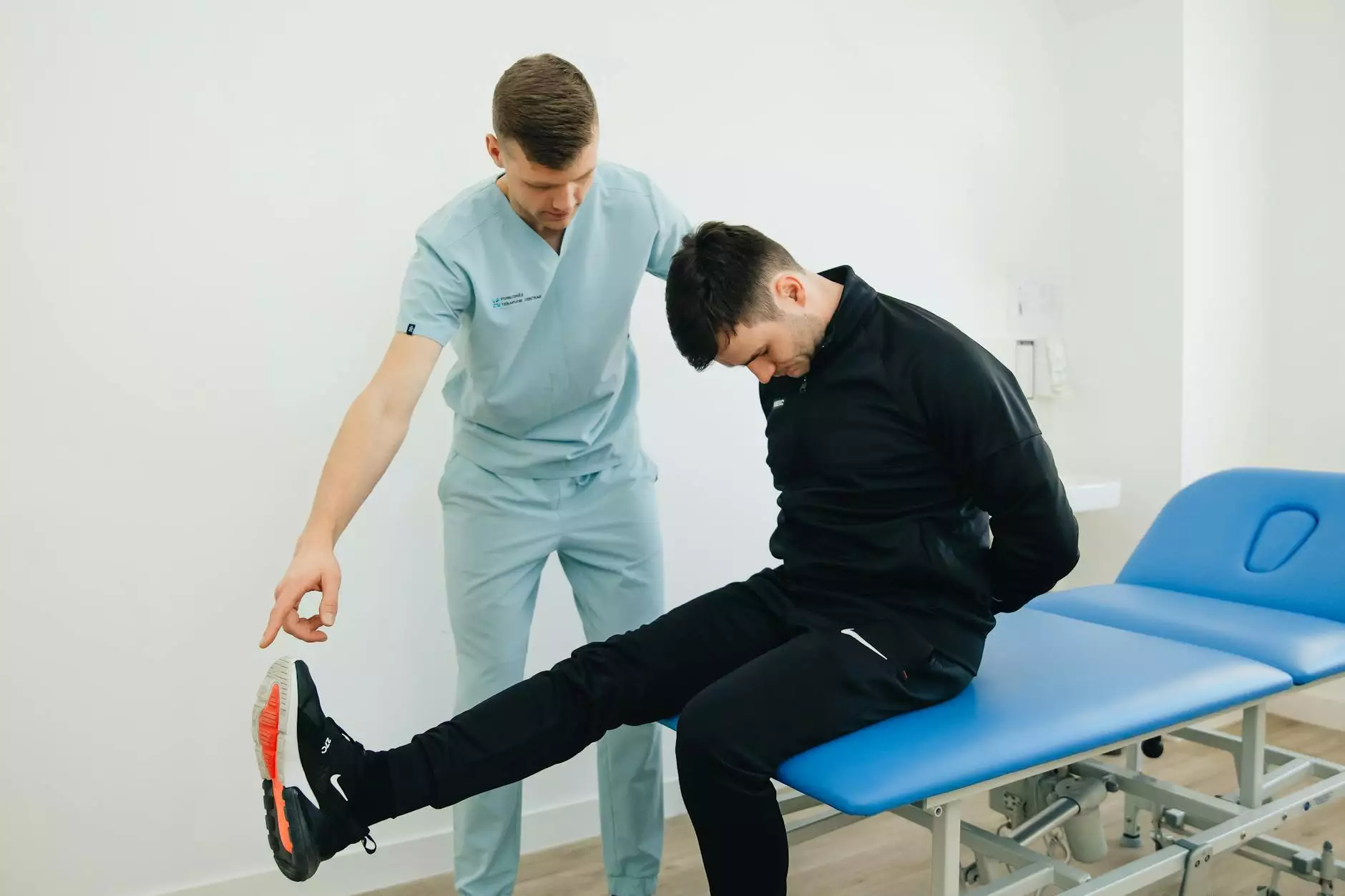
The glenohumeral joint capsular pattern is a critical concept in the fields of health and rehabilitation, particularly for professionals such as chiropractors and physiotherapists. Understanding this pattern is essential for the effective treatment of shoulder disorders and injuries. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the anatomy of the glenohumeral joint, explore the capsular pattern, discuss its significance in clinical practice, and provide insights into treatment strategies that can enhance patient outcomes.
What is the Glenohumeral Joint?
The glenohumeral joint, commonly known as the shoulder joint, is a ball-and-socket joint that allows for a wide range of motion in the arm. It consists of:
- The Glenoid: A shallow socket on the scapula (shoulder blade) that forms the glenohumeral joint with the spherical head of the humerus.
- The Humeral Head: The rounded top of the humerus that fits into the glenoid, allowing for significant mobility.
- Joint Capsule: A fibrous structure that surrounds the joint, providing stability and containment for the synovial fluid, which lubricates the joint.
This construction allows the shoulder to perform various movements, including flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, internal rotation, and external rotation.
Understanding the Capsular Pattern
The term capsular pattern refers to a predictable pattern of restriction of joint movement caused by conditions that affect the joint capsule. In the case of the glenohumeral joint, this capsular pattern is essential for clinicians to recognize, as it provides crucial diagnostic information. A typical capsular pattern for the glenohumeral joint is:
- Loss of external rotation
- Loss of abduction
- Loss of internal rotation (less severe)
This sequence indicates that external rotation is the most limited motion, followed by abduction, and finally internal rotation. Recognizing this pattern aids healthcare providers in diagnosing conditions such as adhesive capsulitis (frozen shoulder), rotator cuff injuries, and other shoulder joint disorders.
The Importance of the Glenohumeral Joint Capsular Pattern in Clinical Practice
Understanding the glenohumeral joint capsular pattern is imperative for several reasons:
1. Diagnostic Accuracy
Identifying the specific limitations in joint motion helps practitioners determine the underlying pathology. For example:
- Adhesive Capsulitis: Presents with significant limitations in external rotation and abduction.
- Rotator Cuff Tear: May exhibit decreased motion but often shows different patterns based on the extent of the injury.
2. Treatment Planning
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, knowing the capsular pattern assists in forming an appropriate treatment plan, which may include:
- Physical Therapy: Focusing on restoring lost range of motion through specific exercises.
- Chiropractic Adjustments: Aiming to improve joint function and reduce pain.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques designed to mobilize the joint capsule and surrounding tissues.
3. Rehabilitation Techniques
Effective rehabilitation hinges on understanding which movements are restricted. A tailored program might include:
- Passive Range of Motion Exercises: To initiate movement without stressing the joint.
- Active Range of Motion Exercises: Gradually introducing motion into the restricted phases.
- Strengthening Exercises: To build the surrounding musculature once motion is restored.
Common Conditions Affecting the Glenohumeral Joint
Several conditions can lead to alterations in the glenohumeral joint capsular pattern:
- Rotator Cuff Injuries: Inflammation or tears in the rotator cuff muscles can lead to changes in shoulder mobility.
- Adhesive Capsulitis: Characterized by stiffness and pain, this condition results in significant loss of shoulder motion.
- Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: Compression of the rotator cuff tendons can limit arm elevation and rotation.
- Arthritis: Degenerative changes in the joint can also affect motion quality and quantity.
Assessment Techniques for Glenohumeral Joint Disorders
To evaluate glenohumeral joint function and identify any capsular restrictions, healthcare providers utilize several assessment techniques:
- Active and Passive Range of Motion Tests: Evaluating the degree of motion available in various directions.
- Special Tests: Such as the Hawkins-Kennedy test for impingement or the Neer test.
- Functional Movement Screening: Assessing how the shoulder performs in activities of daily living and sports.
Effective Treatment Modalities
Once the condition has been diagnosed based on the capsular pattern and assessment findings, various treatment modalities can be employed:
1. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is often the first line of treatment. Key components include:
- Stretching: Gentle stretching exercises to gradually increase range of motion.
- Strengthening: Building strength in the shoulder girdle to support and stabilize the joint.
- Posture Correction: Addressing any postural issues that may contribute to shoulder pain.
2. Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic adjustments can restore proper alignment and biomechanics of the shoulder joint, enhancing function and reducing pain. Specific techniques may include:
- Spinal Adjustments: Impacting overall body mechanics and nervous system function.
- Shoulder Manipulations: Targeting the shoulder joint to improve motion.
3. Alternative Therapies
Additional therapies can support traditional treatment methods:
- Acupuncture: May provide pain relief and promote healing.
- Massage Therapy: Aiding in muscle relaxation and reduced tension.
Rehabilitation and Recovery: The Road to Recovery
Recovering from glenohumeral joint disorders requires a well-structured rehabilitation program. Key factors include:
- Individualized Programs: Tailoring rehabilitation to the specific needs of the patient and their particular condition.
- Progress Monitoring: Regular reassessment to ensure the treatment plan is effective and adjust as needed.
- Patient Education: Informing patients about proper body mechanics and prevention strategies to avoid recurrence.
Conclusion
Understanding the glenohumeral joint capsular pattern is essential for healthcare practitioners involved in the treatment of shoulder disorders. It allows for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment planning, and comprehensive rehabilitation strategies. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, professionals must remain informed about these patterns and their implications in patient care. By prioritizing education and employing a variety of treatment modalities, we can enhance patient outcomes and promote lasting recovery.
For more information on enhancing your practice with effective techniques related to the glenohumeral joint capsular pattern, feel free to explore further resources and training opportunities provided by IAOM-US.